Understanding Residential and Commercial Roofing
A roof’s purpose is to protect both residential and commercial properties from the earth’s elements. However, specific needs and planning differ significantly between the two. Understanding these differences is essential for roofing contractors, property owners, and anyone involved in the roofing industry. In this blog post, we will explore the distinctions between residential and commercial roofing, including structure and design considerations, materials, function, and maintenance regulations.
Structural design & size
One of the main differences between residential and commercial roofing is the size and structure of the building that hosts them.
Residential: Residential roofs are typically sloped or pitched, with a wide variety of designs, including gable, hip, and mansard. The focus is often on aesthetics and curb appeal, complementing the overall architectural style of the home. Residential roofs are generally smaller in size and feature multiple slopes.
Commercial: Commercial roofs are typically flat or low-sloped, allowing for larger surface areas. The design is more functional and aims to accommodate HVAC systems, vents, and other equipment. Commercial roofs may have fewer design variations and focus primarily on durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness
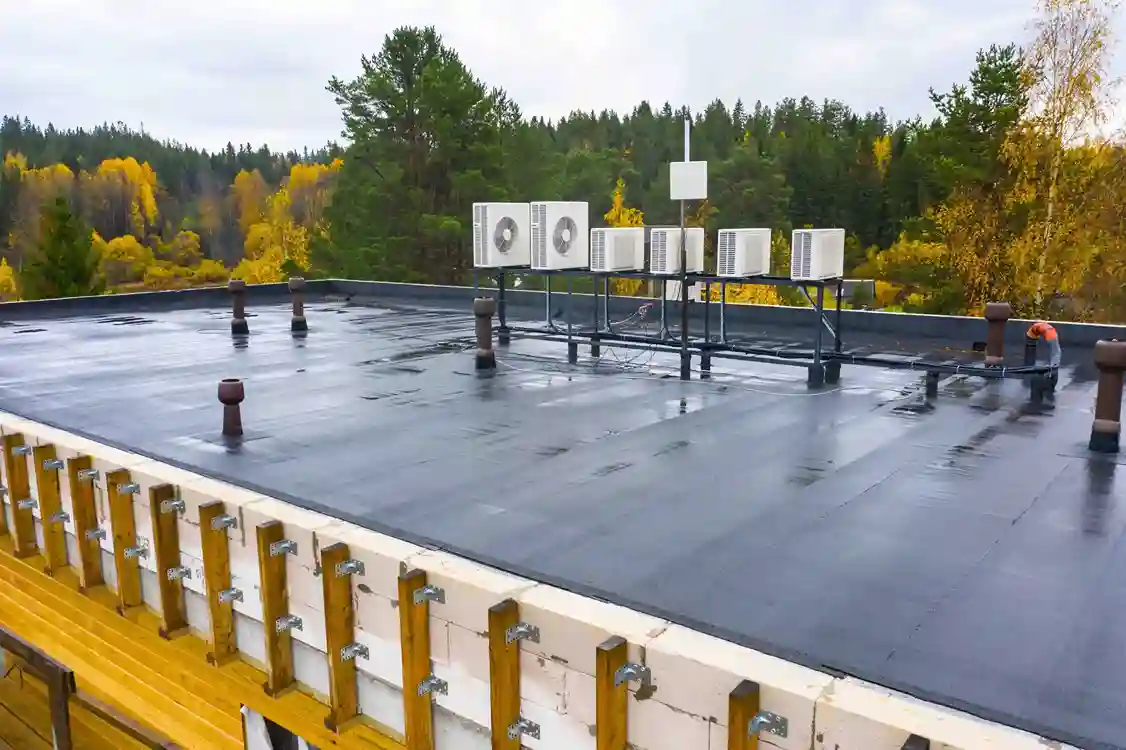



Materials & construction
The choice of roofing materials for residential and commercial properties also differs.
Residential: Residential roofs commonly use materials such as asphalt shingles, wood shakes, clay or concrete tiles, or metal roofing. These materials are chosen for their aesthetic appeal, durability, and affordability. Residential roofs often involve more intricate installation techniques due to the variety of architectural styles.
Commercial: Commercial roofs typically use materials like modified bitumen, single-ply membranes (such as EPDM, TPO, or PVC), metal roofing, or built-up roofing (BUR) systems. These materials offer excellent durability, waterproofing, and energy efficiency. Commercial roofs may require additional layers or insulation to meet specific building codes and regulations.
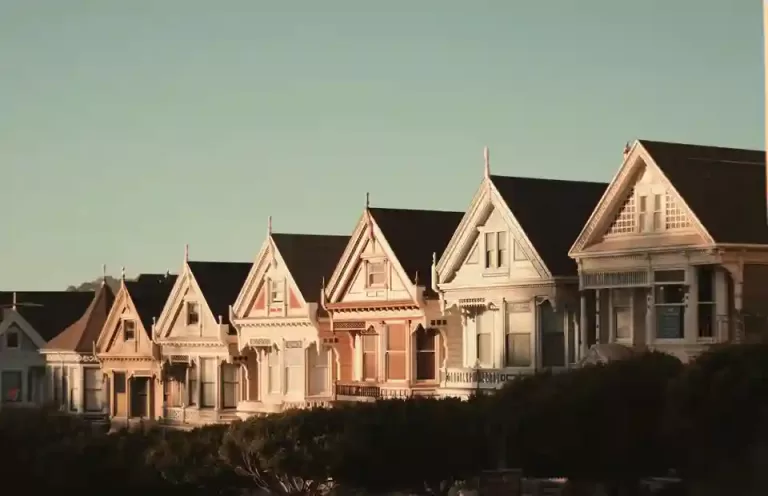
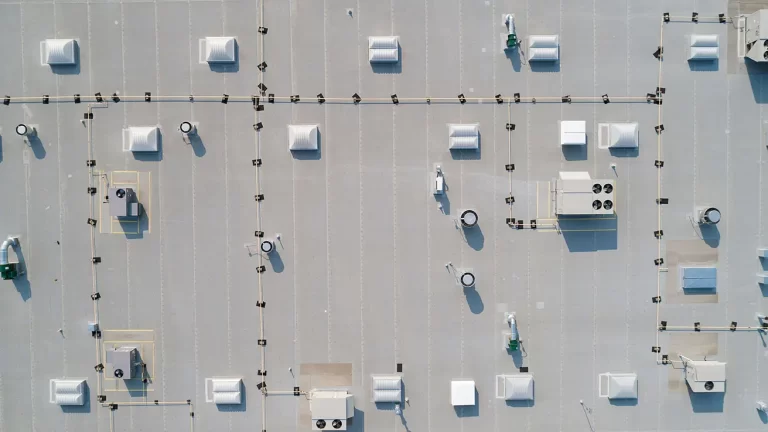


Functionality & longevity
Residential and commercial roofs serve different purposes and have varying lifespan expectations.
Residential: Residential roofs primarily provide protection from the elements while enhancing the home’s appearance. Although durability is essential, residential roofs typically have a shorter lifespan compared to commercial roofs, typically ranging from 20 to 30 years.
Commercial:
Commercial roofs are designed to withstand heavier foot traffic, accommodate equipment installations, and provide long-lasting protection. They are built with materials that offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Commercial roofs can last anywhere from 20 to 50 years, depending on the materials used and maintenance practices.
Maintenance & regulations
There are also a few differences when it comes to maintaining residential vs. commercial roofs.
Residential: Residential roofs require regular inspections for damaged shingles, leaks, or gutter issues. Maintenance often includes gutter cleaning, tree limb removal, and occasional repairs. Residential roofing regulations are typically less stringent, with more flexibility in design and materials.
Commercial: Commercial roofs often require regular inspections by professionals due to their larger size and complexity. Maintenance tasks may involve checking for leaks, repairing flashing, maintaining HVAC systems, and removing debris. Commercial roofing is subject to stricter regulations and compliance with building codes, fire safety standards, and energy efficiency requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between residential and commercial roofing is imortant for property owners and roofing professionals alike. From structural design to materials, functionality, and maintenance, each type of roofing has its own considerations. By recognizing these distinctions, property owners can make informed decisions when it comes to installation, repairs, and maintenance, ensuring that their roofs provide optimal protection and longevity for their specific property type. Likewise, roofing contractors can tailor their services to meet the specific needs of residential or commercial clients, offering the most effective solutions for each category